F: Ejercicios resueltos¶
Ejercicio F.1:
Mejorar la función que calcula la fotometría para restar el fondo utilizando un anillo alrededor de la estrella CircularAnnules. Para ello habrá que calcular el brillo medio de dicho anillo y restarle a las cuentas de la estrella el brillo medio multiplicado por el área de la apertura (aperture.area).
[1]:
def doPhotometry2(data, positions):
aperture = CircularAperture(positions, r=3.) # Fotometría en un círculo de radio 3
apertureBackground = CircularAnnulus(positions, r_in=5., r_out=7.) # Anillo de radios 5 y 7 para calcular el fondo local de la fuente
photTable = aperture_photometry(data, aperture) # Hacemos ambas fotometrías
photTableBackground = aperture_photometry(data, apertureBackground) #
avgBackground = photTableBackground['aperture_sum'] / apertureBackground.area # Calculamos la media del fondo
newPhotTable = photTable['aperture_sum'] - (avgBackground * aperture.area) # Le restamos a la fuente el fondo
res = newPhotTable.tolist()
return res
Ejercicio F.2:
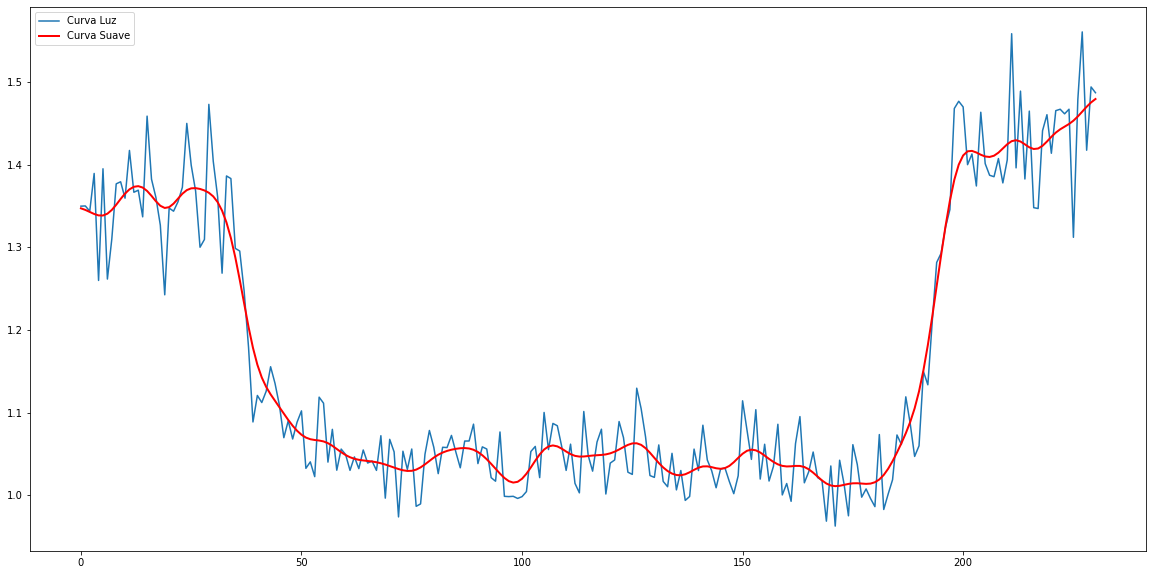
Suavizar la curva de luz obtenida usando una convolución.
[3]:
from astropy.convolution import Gaussian1DKernel, convolve
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
with open('salidas/curvaLuz.json') as fich:
curvaLuz = json.load(fich)
g = Gaussian1DKernel(stddev=3)
curvaSuave = convolve(curvaLuz, g, boundary='extend')
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (20,10)
plt.plot(curvaLuz, label='Curva Luz')
plt.plot(curvaSuave, label='Curva Suave', linewidth=2, color='red')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()